To Set Up a Chroma Key
Set up the chroma key with the source you want to use and adjust the parameters. Ensure that the chroma key output has been selected on a keyer so that you can view the output as you adjust the parameters.
-
Click Navigation Menu > Live Assist > MEs and select the ME and key that you want to set up.
Tip:You can use the same procedure for a MiniME™ or Canvas. You can use the same procedure for a MiniME™.
- Click Key Video and select the video signal you want to use for the key.
-
Click Chroma Key and click CKX for the chroma keyer you want to use. Notice that both the Auto
Select and Chroma Key buttons are on. The chroma key uses an auto select key as the key type.
Tip:Click Show Alpha to have the preview output of the current ME switch to the alpha signal that is being used by the selected keyer. Show alpha is not available for MiniME™ outputs.Tip:Click Key Preview to force the program output of the selected keyer to the preview output of the switcher.Tip:You can also select the chroma keyer as a source on the key bus and click Chroma Key to navigate to the Chroma Key Parameters page. You can also press the user select button assigned to the chroma key or press and hold the CHR KEY button and press the corresponding keyer button.
-
Click CK Params.
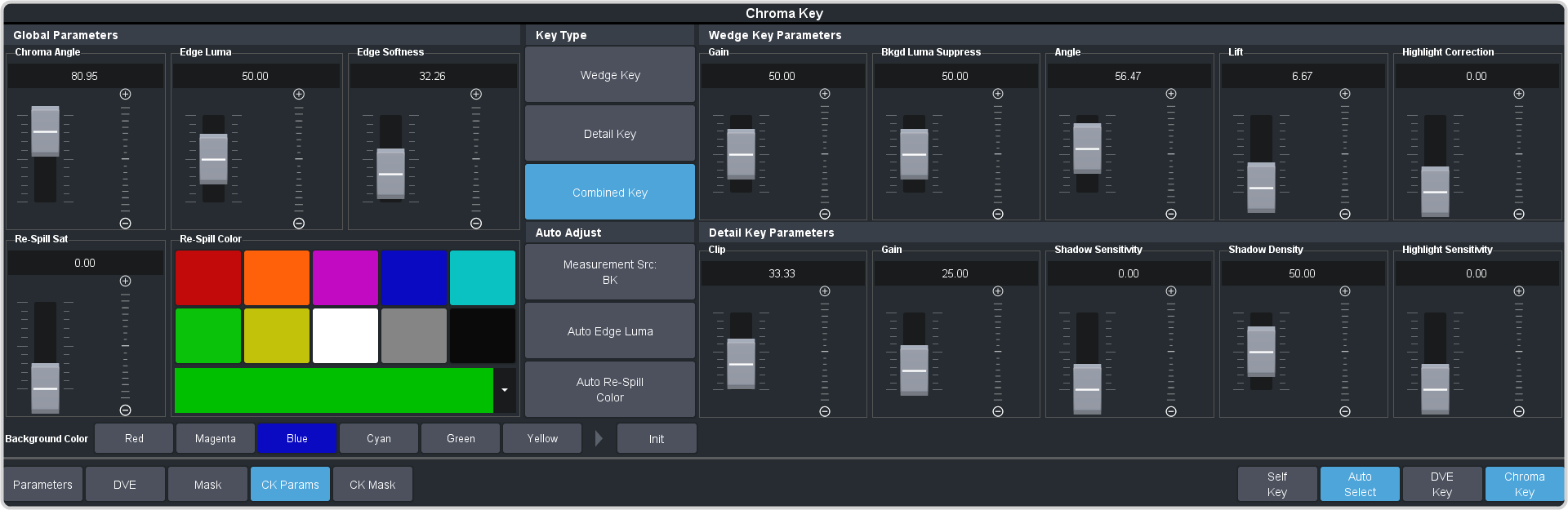
-
Click CK Source and select the video source you want to use for the chroma key. As the key type is an auto select key, the Key Fill is
the chroma keyer and the alpha is replaced with the CK Source selection.
Note:You can only select a physical input, Media-Store, MediaWipe, or clip player for a chroma key. You can also select an Aux Bus or a bus follow, but the source selected on the Aux Bus or follow must be valid for the chroma key.
- Click the Color button for the color of the background you are using for your chroma key.
-
Click Init.
The chroma key engine initializes and attempts to remove the selected background color from the video. Any further adjust is only required if you want to adjust aspects of the key.
-
Click the Key Type button for the chroma key mode you want to use.
- Wedge Key — Based on the standard chroma keyer and discriminates between the color vector angle and level of the background color vs the color vectors and levels in the foreground components.
- Detail Key — Differs from the standard chroma keyer in that it adds luminance dependency to a three-dimensional spherical color discriminator.
- Combination Key — Combine the two modes to offer good capture of high luma detail in the edge regions as well as compensation for similar foreground and background levels.
Note:All adjustments are always available, even if they are not applied by the selected mode.Tip:Although adjustment can be made to either key type while the combined output is selected, it is recommended that adjustments of either key type be conducted with only that key type selected. This eliminates the possibility of the combined key type hiding or concealing the result of adjustments. -
Click Detail Key and adjust the Detail Key Parameters as follows:
Tip:The Detail key type is layered over the Wedge key type and has the largest contribution to the final key-edge quality.
- Clip — use this setting to clip between the foreground and background. You are looking to achieve complete background removal.Tip:Clip should be set to the point where the background is just removed. Setting it too high will reduce edge quality.
- Gain — use this setting to lift the fill image. You are looking to achieve solid fill content.Tip:Setting the gain too high may introduce dark boundaries.
- Shadow Sensitivity — use this setting to adjust the level of dark image areas, particularly in cast shadow areas.
- Shadow Density — use this setting to adjust the apparent lightness of the dark / shadow areas in conjunction with the Shadow Sensitivity.
- Highlight Sensitivity — use this setting to fill areas with specular highlights, such as reflective surfaces, that can show through to the background.
- Clip — use this setting to clip between the foreground and background. You are looking to achieve complete background removal.
-
Click Wedge Key and adjust the Wedge Key Parameters as follows:
- Gain — use this setting to set the Angle Control to 100 and the Lift to
0 and then adjust this setting until the background is fully removed, leaving a reasonable edge to the key. Too much gain will produce hard and undesirable
edges.Tip:Adjust the Gain with the Bkgd Luma Suppress to balance between background removal and edge quality.
- Bkgd Luma Suppress — use this setting to compensate for uneven color or lighting in the shot to ensure the chroma background is fully suppressed.Tip:Turn on a box mask in the keyer you are using to view the chroma key output to compare the backgrounds. The masked area shows the background source without the key settings applied.
- Angle — use this setting to change the color wedge angle (wedge shape) that is used to detect areas of foreground (fill) and background (alpha) based on the chosen color vector. This can help fill in areas of heavy spill without hardening edge detail.
- Lift — use this setting to amplify the generated alpha signal to fill in areas of transparency.
- Highlight Correction — use this setting to lift areas of the image might contain high luminance levels at edge boundaries. This could be due to lighting conditions, camera setup, or subject.
- Gain — use this setting to set the Angle Control to 100 and the Lift to
0 and then adjust this setting until the background is fully removed, leaving a reasonable edge to the key. Too much gain will produce hard and undesirable
edges.
-
Adjust the Global Parameters as follows:
- Chroma Angle — use this setting to select the fill color that has been detected as color spill. You should not have to adjust this setting.
- Edge Luma — use this setting to offset the detected level of the chroma background and allow for fine tuning.Tip:Click Auto Edge Luma to have the switcher automatically adjust the edge luminance.Tip:If the subject image contains fine detail such as fine hair with a luminance level that is close in value to the chroma set color background level – it may be difficult to provide good separation between background and foreground elements.
- Edge Softness — use this setting to filter the edges to eliminate undesirable hard edges and add realism to a scene by simulating depth of field characteristics.
- Re-Spill — use the Re-Spill Color and Re-Spill Sat settings to select a color that is near the average color
of the background/lighting that needs to be added into those areas of the fill that contain the spill from the chroma set.Tip:Click Auto Re-Spill Color to have the switcher automatically adjust the re-spill colors based on the Measurement Src selection.
-
Use the automatic adjustments as follows:
Tip:The Auto Adjust allows you to have the chroma keyer continuously measure the replacement background, the background you are keying the subject onto, used in the final composite.
- Click Measurement Src and select the video source that you want to place the chroma key over. This source is used for the automatic adjustment of the chroma key.
- Click Auto Edge Luma to have the edge luminance automatically adjusted, based on the replacement background.
- Click Auto Re-Spill Color to have the re-spill color automatically adjusted, based on the replacement background.
